Link ad
Followers
Monday, January 31, 2022
Saturday, January 29, 2022
Friday, January 28, 2022
Monday, January 24, 2022
Thursday, January 20, 2022
pH value of common substances
▪️ जल का pH मान कितना होता है = 7
▪️ दूध का PH मान कितना होता है = 6.4
▪️ सिरके का PH कितना होता है = 3
▪️ मानव रक्त का pH मान = 7.4
▪️ नीबू के रस का pH मान = 2.4
▪️ NaCl का pH मान = 7
▪️ pH पैमाने का पता किसने लगाया = सारेन्सन ने
▪️ अम्लीय घोल का pH मान कितना होता है = 7 से कम
▪️ उदासिन घोल का pH मान = 7
▪️ शराब का pH मान = 3.5
▪️ मानव मूत्र का pH मान = 4.8 - 8.4
▪️ समुद्री जल का pH मान = 8.1
▪️ आँसू का pH मान = 7.4
▪️ मानव लार का pH मान = 6.5 - 7.5
🌐
Effects of Hydrogen Bonding on Physical Properties
(i) Boiling point and melting point
a. The boiling point of covalent compounds increases with increase in molecular weight and thus H20 (mol. wt. =18) should have low boiling point than H2S
b. Boiling point of HF (liquid) is greater than boiling . point of HCI (gas) .
c. NH3 has high boiling point than PH3
d. Alcohols: (R-OH) have high boiling point than those of corresponding thioalcohols (R-SH, mercaptans) and ethers (R-O-R).
e. b.pt. of water (100°C) is higher than ethyl alcohol (78°C) because greater number of water molecules are associated (through H-bonding) than the ethyl alcohol.
f. Polyhydric alcohols have higher boiling points than their ethers, inspite of increase in the molecular masses of ethers.
g. Boiling points of aldehydes and ketones are lower than alcohols.
h. The boiling points of primary (R-NH2) and secondary amines (R2NH) are higher than the isomeric tertiary amines (R3N) because like water and alcohols, the primary and secondary amines are capable of forming intermolecular hydrogen bonding but tertiary amine does not.
(ii). Solubility in water-
A hydrogen-bonded organic compound is usually soluble in another hydrogen-bonded substance. So, compounds whose molecule can form H-bonds with water molecule are soluble in water.
a. lower members of alcohols, acids, primary and secondary amines, phenols and carbonyl compounds ate more soluble in water, whereas alkanes, ethers and thiols are insoluble in water.
(iii). States of matter-
H20 is liquid (high boiling point) and H2S is gas. Because in water molecule, hydrogen bonding is present and so become more compact and requires more energy to get them separated during evaporation, while sulphur is less electronegative nature than oxygen and give S-H bond, a smaller ionic character than the O-H bond and thus H2S forms very weak hydrogen bond
(iv). Stereo isomerism:
the trans-isomer of indigo is so stabilised by H-bonding that it resists photochemical isomerisation to the cis-isomer,
(v). Adsorption: Intermolecular H-bonding plays a very important role in the process of dyeing of textiles.
(vi). Hydrogen bonding In biological systems: H-bonding in biological systems also plays an important role and stabilizes usual structure of proteins and nucleic acids.
Wednesday, January 19, 2022
Tuesday, January 18, 2022
HYDROGEN BONDING IN ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
In 1920 Latimer and Rodebush introduced the idea of "hydrogen bond" to explain the nature of association in liquid state of substances like water, hydrogen fluoride, ammonia and formic acid, etc. In a hydrogen compound, when a hydrogen atom lies between two atoms having high electronegativities, it shows a unique property of forming a bond or a bridge between them, holding one of the atoms by a covalent bond and other by purely electrostatic forces (dipole-dipole attraction). This chemical combination between highly electronegative atoms of small atomic radius, such as F and N through a hydrogen bond is referred to as Hydrogen bond or Hydrogen bridge.
Hydrogen bond is defined as "an electrostatic attractive force between the. covalent bonded hydrogen atom of one molecule and an electronegative atom (such as F, 0, N) of the 'other molecule
Nature and Importance of Hydrogen Bonding
(i) Hydrogen bond is merely an electrostatic force rather than a chemical bond.
(ii) Hydrogen bond never involves more than two atoms.
(iii) Bond energy of hydrogen bond is in the range of 3 to 10 Kcal/mol or 10 to 40 kJ/moI, i. e., about 1/10th the energy of a covalent bond. .
(iv) With the increase of electronegativity of the atom to which hydrogen is covalently linked, the strength of' the hydrogen bond increases.
(v) All the three atoms in X -H- - -X lie in a straight line.
Decreasing order of electronegativity of F>O>CI=N>Br>C>H
Electronegativity of an atom is a measure of its power to attract electrons that it is sharing in a covalent bond.
The decreasing order of electronegativity of some common atoms which are generally encountered in organic chemistry is:
F > O > CI= N > Br > C > H
Major sources of organic compounds
There are two major sources of organic compounds:
(I) Natural and
(II) Synthetic.
I) Natural
a).Plants- Carbohydrates (glucose, sucrose, starch, cellulose), acids, esters, vegetable oils, vitamins, gums, alkaloids, essential oils, perfumes, alcohol, acetone, etc. are some of the important organic compounds which are obtained from plants.
b).Animals- Some of the important organic compounds which are derived from 'animals; are proteins, hormones, fats and urea,
c).Fungi and microorganisms-This is the ·source responsible for the· production of hosts of useful substances like alcohols, acids, antibiotics (penicillin, streptomycin, tetracycline) 'and" vitamins by using the process of fermentation.
c). Coal - Coal-tar obtained during destructive distillation of coal is the main source of aromatic hydrocarbons, phenols, heterocyclic compounds, dyes drugs; perfumes, etc.
d). Natural gas and petroleum - It is one of the major sources of organic compounds Gasoline, kerosene, lubricating oil, Vaseline, paraffin wax, etc., ate few examples which are obtained directly from petroleum by fractional distillation. Hundreds of useful organic compounds are prepared from the wide range of hydrocarbons which serve as starting materials for the synthetic reactions.
II). Synthetic Sources- More than 90% of the known organic compounds are synthetic, i.e., prepared by artificial methods. Simple organic ·compounds derived from petroleum and coal have been converted into useful products by synthetic methods.
Now-days, many of the natural products such as dyes, fibres, rubber, drugs, vitamins, etc., are prepared by synthetic reactions.
Monday, January 17, 2022
Catenation
Catenation is the property of atom of an element that may be defined as the self-linking of atoms of an element to form chains and rings. it depends upon the value of bond energy which is maximum in the case of carbon.
C- C > Si-Si > S-S > P-P > N-N > O-O
{ Bond energy (in Kj/mol) as 83,54,54,50,39,35 respectively}
The stability or strength of the bond decreases as the bond energy decreases hence the tendency of catenation decreases following-
C > Si = S > P > N > O
Vital force
Berzelius assumed that some vital force (life force) was necessary to produce organic compounds and synthesis of these compounds in the laboratory was impossible due to the absence of this vital force which only existed in living organisms.
The vital force theory suffered the first deathblow, in 1828, when Fedrick Wohler synthesised first organic compound, urea, in the laboratory by heating ammonium cyanate (an inorganic compound).
NH4CNO + heat 🠚 NH2CONH2 (Urea)
A further blow to vital force theory was given by Kolbe, in 1845, when he synthesised acetic acid, the first organic compound, in laboratory from its elements and . later by Berthelot, in 1856, who synthesised methane.
Sunday, January 16, 2022
CONDUCTANCE OF ELECTROLYTIC SOLUTIONS
☝The electrical resistance of any object is directly proportional to its length, l, and inversely proportional to its area of cross section, A. That is,
R =ρl/A.
☝The inverse of resistance is called conductance, G.
G = l/R = A/lρ =k A/l.
☝The SI unit of conductance is siemen, represented by ‘S’ or Ω-1.
☝The inverse of resistivity is called conductivity (specific conductance) κ.
FACTORS AFFECTING IONIC CONDUCTANCE
(i) The nature of the electrolyte added.
(ii) Size of the ions produced and their solvation.
(iii) The nature of the solvent and its viscosity.
(iv) Concentration of the electrolyte.
(v) Temperature (it increases with the increase of temperature).
Saturday, January 15, 2022
List of Nobel Prize Winners from India
😃भारत से नोबेल पुरस्कार विजेताओं की सूची
1. Rabindranath Tagore : Literature : 1913
2. C.V. Raman : Physics :1930
3. Har Gobind Khorana : Medicine : 1968
4. Mother Teresa : Peace : 1979
5. Subrahmanyam Chandrasekhar : Physics : 1983
6. Amartya Sen : Economic : 1998
7. Venkatraman Ramakrishnan : Chemistry : 2009
8. Kailash Satyarthi : Peace : 2014
9. Abhijit Banerjee : Economic : 2019
Sunday, January 2, 2022
General science-Important questions for competition part-1
1. जीव तथा जंतु विज्ञान का जनक अरस्तु है।
2. विज्ञान शब्द का प्रयोग सर्वप्रथम लैमार्क (फ्रांस) और ट्रेविरनेस (जर्मनी) ने किया।
3. जैव विकास को सर्वप्रथम लैमार्क ने समझाया।
4. चिकित्सा शास्त्र का जनक हिप्पोक्रेटस है।
5. वनस्पति विज्ञान का जनक थियोफ्रेस्ट्स है।
6. रसायन विज्ञान का जनक लेवोजियर है।
7. मानव का विकास, इतिहास, परंपराओं से संबंधित विषय एंथ्रोपोलॉजी कहलाता है।
8.गैसों के विसरण के नियम का प्रतिपादक ग्राहम है।
9. ग्रहों के गति के नियम का प्रतिपादन जॉन्स केप्लर ने किया था।
10. E=mc² का समीकरण आइंस्टीन ने दिया था।
सामान्य विज्ञान : एक लाइनर 02 (#Hindi)
11. जड़त्व के नियम की खोज गैलिलियो ने की थी।
12. गुरुत्वाकर्षण के नियम के प्रतिपादक न्यूटन है।
13. ‘प्राकृतिक वरण सिद्धांत' के प्रतिपादक डार्विन है।
14. उत्परिवर्तन का सिद्धांत ह्यूगो-डी-ब्रीज ने दिया।
15. नेचुरल सेलकक्यान' का सिद्धांत डार्विन ने दिया।
16. विकास के सिद्धांत के प्रतिपादक चार्ल्स डार्विन है।
17. आनुवांशिकी के जनक ग्रेगर जॉन मेंडल है।
18. मेंडल ने अपने प्रयोग के लिए मटर के पौधे का चयन किया था।
19. आनुवंशिकता के विज्ञान को 'आनुवंशिकी (Genetics)' डब्ल्यू वाटसन ने कहा था।
20. आनुवंशिकी उत्परिवर्तन क्रोमोसोम में होता है।
21. सर्वप्रथम 'जीन' शब्द का प्रयोग जोहान्सन ने किया था।
22. जीन (Gene) गुणसूत्रों में अवस्थित होते है।
23. ‘एक जीन एक एंजाइम' सिद्धांत को प्रतिपादित बीडल एवं टैटम ने किया था।
24. खून का रंग लाल हीमोग्लोबीन के कारण है।
25. हीमोग्लोबिन में पाया जाने वाला तत्त्व लोहा है।
26. हीमोग्लोबीन प्रोटीन का यौगिक है।
27. हीमोफीलिया रोग में खून थक्का नहीं जमता है।
28. शरीर के अंदर रक्त को जमने से हिपैरीन नामक प्रोटीन रोकता है।
29. हिपैरनी (Heparin) नामक प्रोटीन का उत्पादन यकृत द्वारा होता है।
30. रक्त का अध्ययन हेमाटोलॉजी कहलाता है।
31. रक्त के थक्का बनने में प्लेटलेट्स सहायक है।
32. प्लेटलेट्स की मृत्यु प्लीहा में होती है।
33. रक्त का थक्का जमाने में सहायक विटामिन K है।
34. रूधिर का तरल भाग प्लाज्मा होता है।
35. रक्त का 60% भाग प्लाज्मा होता है।
36. पदार्थ की चतुर्थ अवस्था प्लाज्मा है।
37. रक्त में पाई जाने वाली धातु लोहा है।
38. प्लीहा ( Spleen) ‘ब्लड बैंक' कहलाता है।
39. RBC का कब्रागाह (शमशान) प्लीहा है।
40. स्वस्थ मनुष्य के शरीर में रक्त का औसत 5 - 6 लीटर होता है।
41. रक्त समूह A, B, AB, O होते हैं।
42. रक्त समूह की खोज लैंडस्टीनर ने की थी।
43. सर्वदाता रक्त समूह O है।
44. सर्वग्राही रक्त समूह AB है।
45. आर. एच. फैक्टर रक्त से संबंधित है।
46. Rh फैक्टर के खोजकर्ता लैंड स्टीनर एवं वीनर है।
47. रक्त चाप एड्रिनल ग्रन्थि से नियंत्रित होता है।
48. वृक्क (Kidney) रक्त को शुद्ध करता है।
49. रक्त के शुद्धिकरण की प्रक्रिया डायलेसिस है।
50. वृक्क में मूत्र का निर्माण होता है।
51. वृक्क (Kidney) का भार 150gm होता है।
52. मानव गुर्दे (Kidney) में बनने वाली पथरी कैल्सियम ऑक्जेलेट की बनी होती है।
53. रक्त (क्षारीय) का pH मान 7.4 होता है।
54. रक्तदाब मापने वाला यंत्र स्फिग्नोमैनोमीटर है।
55. सर्वप्रथम रक्त परिसंचरण तन्त्र का अध्ययन विलियम हार्वे ने किया था।
56. शरीर से हृदय की ओर रक्त ले जानेवाली रक्तवाहिनी शिरा कहलाती है।
57. हृदय से शरीर की ओर रक्त ले जानेवाली रक्तवाहिनी धमनी कहलाती है।
58. हृदय की धड़कन का नियंत्रक पेसमेकर है।
59. जराविक-7 कृत्रिम हृदय है।
60. शरीर में ऑक्सीजन का परिवहन रक्त द्वारा होता है।
Q.61 पित्त होता है
Ans. पीले-हरे रंग का क्षारीय द्रव
Q.62 पित्त (Bile) का pH मान होता है
Ans. 7.7
Q.63 पित्त स्त्रावित होता है
Ans. यकृत द्वारा
Q.64 यकृत (लीवर) में भविष्य के लिए भंडारित रहता है
Ans. विटामिन A
Q.65 पित्त (Bile) जमा होता है
Ans. पिताश्य में
Q.66 हाइड्रोफोबिया रोग होता है
Ans. कुत्ते के काटने से
Q.67 हाइड्रोफोबिया रोग होता है
Ans. विषाणु द्वारा
Q.68 विषाणु (Virus) की खोज
Ans. इवानेवस्की ने
Q.69 विषाणुओं का अध्ययन है
Ans. वाइरोलॉजी
Q.70 जन्तुओं में होने वाली 'फूट एंड माउथ' रोग होता है
Ans. विषाणु के कारण
Q.71 कवकों का अध्ययन कहलाता है
Ans. माइकोलॉजी
Q.72 शैवालों की कोशिकाभित्ति बनी होती है
Ans. सेल्यूलोज की
Q.73 जीवाणु (Bacteria) की खोज
Ans. ल्यूवेनहॉक ने
Q.74 ध्वनि का वेग सर्वाधिक होता है
Ans. ठोस में
Q.75 ध्वनि की गति धीमी होती है
Ans. हवा में
Q.76 ध्वनि की चाल होती है
Ans. 760 मील/घंटा
Q.77 ताप बढ़ने से ध्वनि की चाल
Ans. बढ़ती है
Q.78 वायु है
Ans. गैसों का मिश्रण
Q.79 वायु उदहारण है
Ans. गैस का गैस में विलयन
Q.80 हवा में ध्वनि का वेग होता है
Ans. 332 मी./से.
Q.81 ध्वनि तीव्रता की इकाई है
Ans. डेसीबल
Q.82 हवा का वाष्प घनत्व होता है
Ans. 14.4
Q.83 प्रकाश वर्ष मात्रक है
Ans. दूरी का
Q.84 एक प्रकाश वर्ष बराबर होता है
Ans. 9.46x1012 किमी. या 9.46x1015 मी.
Q.85 दूरी मापने की सबसे बड़ी इकाई है
Ans. पारसेक
Q.86 जड़ों के रूपांतरण है
Ans. मूली और गाजर
Q.87 तने के रूपांतरण है
Ans. आलू और प्याज
Q.88 पिट्यूटरी ग्रंथि पायी जाती है
Ans. मस्तिष्क में
Q.89 मास्टर ग्रंथि कहलाता है
Ans. पिट्यूटरी (पीयूष)
Q.90 शरीर की सबसे छोटी ग्रंथि है
Ans. पिट्यूटरी
Q.91 दो वंशानुगत रोग है
Ans. वर्णान्धता एवं हीमोफीलिया
Q.92 सर्वप्रथम मनुष्यों में वर्णाधता का वर्णन किया है
Ans. हेरनर ने (1876)
Q.93 एक वर्णान्ध व्यक्ति में पहचान करने की क्षमता नहीं होती है
Ans. हरा एवं लाल रंग की
Q.94 थाइरॉक्सिन हार्मोन स्त्रावित होता है
Ans. थाइरॉयड ग्रंथि से
Q.95 जठर रस में पाया जाता है
Ans. हाइड्रोक्लोरिक अम्ल
Q.96 लाइकेन में परस्पर सहजीवी मौजूद होता है
Ans. कवक और शैवाल
Q.97 प्रोटीन का पाचन होता है
Ans. छोटी आंत में
Q.98 मनुष्य का पाचन प्रारंभ होता है
Ans. मुख से
Q.99 पचे भोजन का अवशोषण होता है
Ans. छोटी आंत में
Q.100 लार में पाया जाने वाला एंजाइम
Ans. टायलिन
Q.101 टिबिया नामक हड्डी पाई जाती है
Ans. टांग में
Q.102 मानव शरीर का वह अंग जिसमें हड्डियों की संख्या सर्वाधिक होती है
Ans. अंगुली में
Q.103 भोजन पचाने में सहायक होता है
Ans. एंजाइम
Q.104 एंजाइम की रचना होती है
Ans. अमीनो अम्ल में
Q.105 पाचन क्रिया में प्रोटीन बदल जाते हैं
Ans. अमीनो अम्ल में
Q.106 आहार नाल में स्टार्च के पाचन में अंतिम उत्पाद है
Ans. माल्टोज
Q.107 शरीर में अमीनो अम्ल की संख्या होती है
Ans. 20
Q.108 शरीर में उत्तकों का निर्माण होता है
Ans. प्रोटीन से
Q.109 हड्डियों और दांतों के निर्माण के लिए आवश्यक तत्व है
Ans. कैल्सियम व फॉस्फोरस
Q.110 भोपाल गैस कांड (1984) में रिसाव हुआ था
Ans. मिथाइल आइसोसाइनाइट का
Q.111 काला हीरा तथा काला शीशा कहते है
Ans. क्रमश: कार्बोनेडो और ग्रेफाइड को
Q.112 जीवन रक्षक हार्मोन कहते हैं
Ans. एड्रीनल को
Q.113 पौधें का मुख्य प्रकाश संश्लेषी अंग है
Ans. पत्ती
Q.114 पत्तियों का रंग हरा होता है
Ans. क्लोराप्लास्ट ( हरित लवक) के कारण
Q.115 पत्तियों का रंग पीला होता है
Ans. कैरोटीन के निर्माण के कारण
Q.116 पर्णहरित (Chlorophull) में उपस्थित मुख्य धातु है
Ans. मैग्नीशियम
Q.117 वायुमंडल में ऑक्सीजन की मात्रा संतुलित होती है
Ans. प्रकाश संश्लेषण द्वारा
Q.118 पेड़ व पौधें द्वारा खाना तैयार करने की प्रक्रिया है
Ans. प्रकाश संश्लेषण (फोटोसिंथेसिस)
Q.119 प्रकाश संश्लेषण के लिए आवश्यक है
Ans. CO², जल, क्लोरोफिल और सूर्य का प्रकाश
Q.120 प्रकाश संश्लेषण की क्रिया सबसे अधिक होती है
Ans. लाल रंग के प्रकाश में
Q.121 प्रकाश संश्लेषण में ऑक्सीजन निकलता (उपचयन होता है) है
Ans. जल से
Q.122 प्रकाश संश्लेषण का प्रथम स्थिर यौगिक है
Ans. फॉस्फोग्लिसरिक अम्ल
Q.123 राइजोम पादप का भूमिगत प्रारूप है
Ans. तना
Q.124 दलहन के जड़(Legume plants root) में पाए जाने वाला जीवाणु है
Ans. राइजोबियम
Q.125 पौधें नाइट्रोजन ग्रहण करते हैं
Ans. नाइटेट के रूप में
Q.126 पादपों में जल तथा खनित लवणों का संचालन होता है
Ans. जाइलम द्वारा
Q.127 पादपों में बना खाद्य पदार्थ पौधे के विभिन्न अंगों में पहुँचता है
Ans. फ्लोएम द्वारा
Q.128 वह यंत्र जिसके द्वारा तने की वृद्धि दर नापी जाती है, वह है
Ans. ऑकजेनोमीटर(oxanometer)
Q.129 आत्महत्या की थैली' (suicidal bags) कहलाता है
Ans. लाइसोसोम( Lysosome)
Q.130 लाइसोसोम की खोज की
Ans. डी- डुबे ने 1949 में
Q.131 प्रोटीन की फैक्ट्री कहलाता है
Ans. राइबोसोम(Ribosomes)
Q.132 प्रोटीन का संश्लेषण होती है
Ans. राइबोसोम द्वारा
Q.133 DNA की खोज की थी
Ans. वाटसन एवं क्रिक ने
Q.134 DNA संश्लेषण का प्रतिपादन किया
Ans. कॉर्नबर्ग
Q.135 DNA और RNA है
Ans. न्यूक्लिक अम्ल
Q.136 DNA के क्रियात्मक खंड को कहते हैं
Ans. जीन
Q.137 DNA का डबल हेलिक्स मॉडल(DNA double helix model) को बनाया था
Ans. वाटसन एवं क्रिक ने
Q.138 DNA की इकाइयां है
Ans. न्यूक्लिओटाइड्स
Q.139 सर्वप्रथम प्रयोगशाला में 'जीन' का संश्लेषण किया था
Ans. हरगोविंद खुराना ने
Q.140 पुरुष व स्त्री संघटन होता है
Ans. XY तथा XX
Q.141. एक लड़का पिता से 'क्रोमोसोम' पाता है
Ans. 22 + Y
Q.142 बच्चे का लिंग निर्धारित होता है
Ans. पिता के गुणसूत्र (XY) द्वारा
Q.143 पैतृकत्ता सिद्ध करने में सहायक है
Ans. DNA और फिंगर प्रिंटिंग टेस्ट
Q.144 मधुमेह रोग होता है
Ans. इन्सुलिन की कमी से
Q.145 इन्सुलिन की खोज की
Ans. वेटिंग एवं वेस्ट ने
Q.146 इंसुलिन शरीर में बनती है
Ans. अग्नाशय द्वारा
Q.147 बॉन्क्राईटिस एक रोग है
Ans. श्वास नली का
Q.148 पेप्सीन का एक उदाहरण है
Ans. एंजाइम
Q_149. दूध में नहीं पाया जाने वाला विटामिन है
Ans. C
Q.150 प्लाज्मोडियम परजीवी है
Ans. मलेरिया रोग का
Que : लाल रक्त कण [Red Blood Cells] का निर्माण होता है ??
Ans - अस्थिमज्जा में
Q.151 मलेरिया रोग का वाहक है
Ans. मादा एनोफेलीज मच्छर
Q.152 मलेरिया रोग में प्रभावित अंग है
Ans. प्लीहा (तिल्ली)
Q.153 मानव मूत्र में उत्सर्जित होता है में
Ans. विटामिन C
Q.154 मूत्र (अम्लीय) का pH मान होता है
Ans. 6
Q.155 मूत्र का रंग पीला होता है
Ans. यूरोक्रोम के कारण
Q.156 मेढ़क के हृदय में होते हैं
Ans. तीन भाग
Q.157 मनुष्य के हृदय में कितने प्रकोष्ठ होते हैं
Ans. चार
Q.158 मानव शरीर में जल की मात्रा शरीर के भार का होता है
Ans. 0.1
Q.159 शरीर में प्रचुर पाया जाने वाला तत्व है
Ans. ऑक्सीजन
Q.160 मनुष्य के शरीर में जल होता है
Ans. 65-80%
Q.161 मानव शरीर का सामान्य ताप होता है
Ans. 98.6°F या 37°C या 310K
Q.162 मनुष्यों में मेरूदंड से कितनी जोड़ी तंत्रिका निकलती है
Ans. 31
Q.163 गुणसूत्र (क्रोमोसोम) की खोज
Ans. वाल्डेयर ने
Q.164 गुणसूत्रों का निर्माण होता है
Ans. क्रोमेटिन नामक पदार्थ से
Q.165 मनुष्य में क्रोमोसोम की संख्या
Ans. 46 (23 जोड़ी)
Q.166 जीवन की सबसे छोटी रचनात्मक एवं कार्यात्मक इकाई है
Ans. कोशिका
Q.167 सबसे छोटी जीवित कोशिका है
Ans. माइकोप्लाज्मा
Q.168 शरीर की सबसे लम्बी कोशिका
Ans. तंत्रिका तन्त्र
Q.169 तंत्रिका तंत्र की रचनात्मक तथा क्रियात्मक इकाई होती है
Ans. न्यूरान
Q.170 कोशिका शब्द का निर्माण
Ans. रॉबर्ट हुक द्वारा
171 : लाल रक्त कण का जीवन काल ?
Ans - 120 दिन
172 : श्वेत रक्त कण [White Blood Cell] का जीवन काल ?
Ans - 1 से 4 दिन
173. : श्वेत रक्त कण [White Blood Cell] को कहा जाता है ?
Ans - ल्यूकोसाइट Leukocytes
174 : लाल रक्त कण [Red Blood Cells] को कहा जाता है ?
एरिथ्रोसाइट Erythrocytes
175 : शरीर का ताप नियंत्रक होता है ?
Ans - हाइपोथैलमस ग्रंथि Hypothalamus Gland
176. : मनुष्य [Human] की सर्वदाता रक्त समूह (Universal Donor) ?
Ans - O
177 : मनुष्य की सर्वग्राही रक्त समूह (Universal Receptor) ?
Ans - AB
178 : रक्तचाप [Blood Pressure] मापने की यंत्र को कहा जाता है ?
Ans - स्फिग्मोमैनोमीटर Sphygmomanometer
179 : ‘ब्लड बैंक [Blood Bank] ‘ कहलाता है ?
Ans - प्लीहा (Spleen)
180 : भोजन का पाचन प्रारंभ होता है ?
Ans - मुख से
181 : पचे हुए भोजन का अवशोषण होता है ?
छोटी आँत Small Intestine में
182 : पित (Bile) स्त्रावित होता है ?
Ans - यकृत Liver द्वारा
183 : विटामिन ‘ए‘ [Vitamin 'A'] संचित होता है ?
Ans - यकृत में
184 : शरीर की सबसे बड़ी ग्रंथि [Largest Gland] ?
Ans - यकृत (लीवर)
185 : सबसे छोटी ग्रंथि [Small Gland] (मास्टर ग्रंथि) ?
Ans - पिट्यूटरी
186 : मनुष्य में पसलियाँ [Ribs] की संख्या होती है ?
Ans - 12 जोड़ी
187 : शरीर में हड्डियों [Bones] की कुल संख्या है ?
Ans - 206
188 : शरीर में मांसपेशियों [Muscles] की कुल संख्या ?
Ans - 639
189 : लार [Saliva] में पाया जाने वाला एन्जाइम [Enzyme] होता है ?
Ans - टायलिन Taylin
190 : लिंग निर्धारण कहां से होता है ?
Ans - पुरूष क्रोमोसोम Men Chromosomes पर
191 : मनुष्य का हृदय [Human Heart] होता है ?
Ans - चार कोष्ठीय
192 : शरीर में गुणसूत्रों (Chromosomes) की संख्या पाई जाती है ?
Ans - 46
193 : शरीर का सबसे बड़ा अंग [Largest Organ] ?
Ans - त्वचा
194 : शरीर की सबसे बड़ी कोशिका ?
Ans - तंत्रिका तंत्र
195 : शरीर में अमीनों अम्ल [Amino Acids] की संख्या ?
Ans - 22
196 : शरीर में प्रतिदिन मूत्र [Urine] बनता है ?
Ans - 1.5 लीटर
197 : मूत्र दुर्गंध देता है, क्योंकि ?
Ans - यूरिया Urea के कारण
198 : मानव मूत्र (अम्लीय) का PH मान है ?
Ans - 6
199 : शरीर का सामान्य तापमान होता है ?
Ans - 98.6 डिग्री फेरेनहाइट 'या' 37 डिग्री सेल्सियस 'या' 310 केल्विन
200 : मानव शरीर में टीबिया [Tibia] नामक हड्डी पायी जाती है ?
Ans - पैरों में
201 : दाँतों और हड्डियों की संरचना के लिये आवश्यक तत्व है ?
Ans - कैल्सियम एवं फाॅस्फोरस
202 : रूधिर को थक्का जमने [Blood Clot] में सहायक होता है ?
Ans - प्लेटलेट्स Platelets
203 : मस्तिष्क तथा सिर के अध्ययन से संबंधित है ?
Ans - फ्रेनोलाॅजी Phrenology
204 : श्वसन के दौरान सर्वाधिक मात्रा में ली गई गैस होती है ?
Ans - नाइट्रोजन
205 : जीवित जीवाश्म [Abundant Gas] कौन होता है ?
Ans - साइकस
206 : मीनीमाता रोग किसके कारण होता है ?
Ans - जल में मरकरी के प्रदूषण से
207 : मानव त्वचा [Human Skin] का अध्ययन करने वाली विज्ञान क्या कहलाती है ?
Ans - डर्मेटोलाॅजी Dermatologist
208 : कीड़ों के अध्ययन करने वाली विज्ञान को कहा जाता है ?
Ans - एण्टोमोलाॅजी Entomology
209 : पित्त [Bile] किस अंग के द्वारा पैदा किया जाता है ?
Ans - यकृत Liver
210 : मानव शरीर में रूधिर बैंक [Blood Bank] का कार्य कौन करता है ?
Ans - तिल्ली Spleen
211 : शरीर में हीमोग्लोबिन [Hemoglobin] का कार्य होता है ?
Ans - आक्सीजन(oxygen) का परिवहन
212 : हीमोग्लोबिन [Hemoglobin] में क्या होता है ?
Ans - लोहा
213 : मानव शरीर में खून किसके उपस्थित के कारण नहीं जमता है ?
Ans - हिपेरिन Hiperin
214 : रूधिर के प्लाज्मा में किसके द्वारा एण्टीबाॅडी निर्मित होती है ?
Ans - लिम्फोसाइट Lymphocytes
215 : लाल रक्त कणिकाओं [RBC] का श्मसान कहा जाता है ?
Ans - प्लीहा को
216 : क्रेब्स चक्र [Krebs Cycle] में किसका संश्लेषण होता है ?
Ans - पाइरूविक अम्ल Pyruvic Acid
217 : मानव शरीर में यूरिया का निर्माण कहाँ होता है ?
Ans - यकृत
218 : रक्त की अशुद्धियाँ किस अंग में जाकर छनती है ?
Ans - वृक्कों में
219 : श्वसन की क्रिया कहाँ सम्पन्न होती है ?
Ans - माइट्रोकाॅण्ड्रिया Mitochondrial
The Novel Which I like Most
The
novel that I like most is "The Old Man and The Sea". It caught my
attention and tempted me to read it repeatedly. The story line is interesting
and eye-catching. It tells the story of an old man who remains unsuccessful in
catching a fish for 84 days but he
doesn't give up. He is quite sure that he can catch a fish one day and works
constantly in pursuit of it. He claims that man can be destroyed but can't be
defeated.
The
idea of this novel is that one should never give up even if the struggle is hard.
We have to show perseverance. We must select a dream and work hard for making
it possible for us. At the outset of this story we know that Santiago is
assisted by a boy who is sent with him by a family to learn fishing. When
Santiago fails to catch a fish for eighty four days, the family takes their
child back and want him to go with another fisherman who has the luck of
catching a fish. However, the boy proves to be loyal for Santiago. He often
comes to help him.
Despite
of all setback that Santiago experiences, he never thinks he cannot catch a
fish. When the 84th day comes. He makes his mind to go as far as he can to
catch the fish. Finally his luck smiles for him. He catches a fish but has
still to fight with it. Because the fish is so big. It takes him two days to
bring that fish to the shore. Although he takes skeleton to the shore because
sharks attack and eat the flesh of fish, yet he has won the battle. He has
caught the fish of big stature which nobody has done before. Tourists come to
take pics and are attracted by the gaint fish. Everyone is surprised and the
boy feels proud of Santiago.
This
inspirational story has won my heart. I too feel that I'm like this old man who
has to pursue a dream of achieving my aim. I also should work hard and should
never give up. After all how can I forget "the man can be destroyed but
can't be defeated".
MOLAR CONDUCTIVITY
MOLAR CONDUCTIVITY
- The conductivity is defined as the conductivity of an electrolyte solution divided by molar concentration
- Molar conductivity = λm = κ/c
- if k is expressed in Sm–1 and the concentration, c in mol m–3 then the unit of λm will be Sm2mol–1.
- If we use Scm–1 as the units for k and mol cm–3, the units of
- concentration, then the units for λm are Scm2mol–1. It can be calculated by using the equation:
- λm (Scm2mol–1) = κ(S cm–1) × 1000 (cm3/L)/molarity (mol/L).
ž OR, 1 Sm2mol–1 = 104 Scm2mol–1
Variation of molar conductivity of an ionic solution with concentration
Variation of molar conductivity of an ionic solution with concentration
- conductivity increases with increase in concentration since it depends on number of ions per volume.
- Molar conductivity increases with decrease in concentration since it depends on mobility of ions.
- When concentration approaches zero, the molar conductivity is known as limiting molar conductivity and is represented by E°m
Kohlrausch law of independent migration of ions and its applications
It states that limiting molar conductivity of an electrolyte is the sum of the individual contributions of the anion and cation of the electrolyte.
ü Thus, if λ°Na+ and λ°Cl - are limiting molar conductivity of the sodium and chloride ions , then the limiting molar conductivity for sodium chloride is given by the equation:
Ë°m(NaCl) = λ°Na+ + λ°Cl -Applications of Kohlrausch law
This law may be used to determine the limiting molar conductivity, ‘λ°m’ degree of dissociation ‘α’ and dissociation constant ‘Ka’ of a weak electrolyte
Faraday’s Laws of Electrolysis
(i) First Law: The
amount of chemical reaction which occurs at any electrode during electrolysis by
a current is proportional to the quantity of electricity passed through the
electrolyte (solution or melt).
(ii)Second Law: The
amounts of different substances liberated by the same quantity of electricity
passing through the electrolytic solution are proportional to their chemical
equivalent weights (Atomic Mass of Metal ÷ Number of electrons required to
reduce the cation).
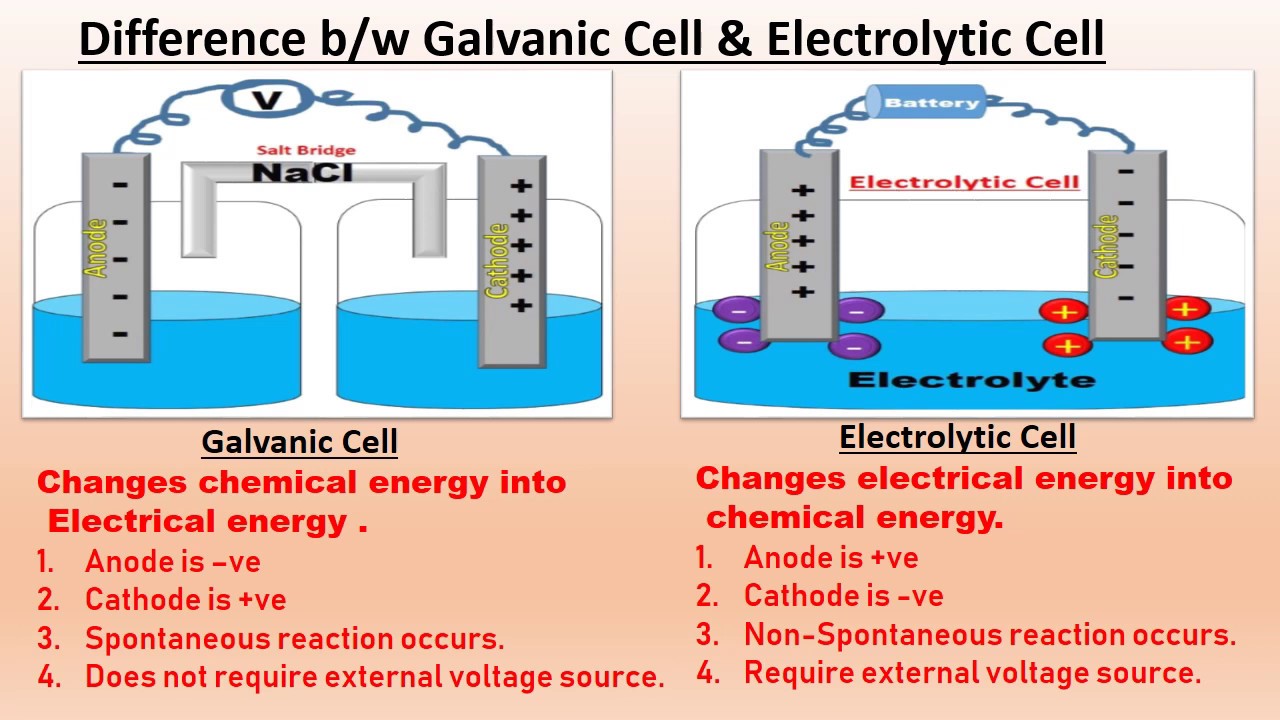
Electrolytic cell
☝This is a device which brings about a chemical change by means of electric current supplied.
☝In this cell two electrodes are dipped in same container.
☝ electricity from outside source supplies electrons for the non-spontaneous reaction.R
☝Reduction takes place cathode where metal from electrolytic solution gets deposited.
ü oxidation takes place anode from where metal goes into the electrolytic solution.
Corrosion And Prevention of corrosion
- Corrosion is the oxidative deterioration of metal.
- 25% of steel produced goes to replace steel structures and products destroyed by corrosion.
- Rusting of iron requires the presence of both oxygen and water.
- Rusting results from tiny galvanic cells formed by water droplets.
Prevention of corrosion
- Galvanizing: is the coating of iron with zinc. Zinc is more easily oxidized than iron, which protects and reverses oxidation of the iron.
- Cathodic Protection: is the protection of a metal from corrosion by connecting it to a metal (a sacrificial anode e.g. Mg or Zn) that is more easily oxidized.
- Electroplating.
- By applying paint, grease, rubber to prevent contact of metal surface from air.
Electrolytic cell and electrolysis
- Electrolysis: It is the process in which electrical energy is used to drive a non-spontaneous chemical reaction.
- An electrolytic cell is an apparatus for carrying out electrolysis.
- Processes in an electrolytic cell are the reverse of those in a galvanic cell.
Electrolysis
process is used in Manufacture of Cl2
and NaOH, Electro-refining and Electroplating, Electrolysis of water
Nernst Equation for a Daniell cell
- Nernst gave a relationship between electrode potentials and the concentration of electrolyte solutions known as Nernst equation.
- Reduction Potential under Non-standard Conditions is determined using Nernst Equation when Concentrations is not-equal to 1M. Thus For the cell,
For Daniel cell,
Zn(s)+Cu2+(aq) 🠊 Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s)
Zn(s)|Zn2+(aq)||Cu2+(aq)|Cu
In Daniell cell, the electrode potential for any given concentration of Cu2+ and Zn2+ ions, we write
For Cathode:
E(Cu2+/Cu) = E0(Cu2+/Cu) – RT/2F ln(1/[Cu2+(aq)]
For Anode:
E(Zn2+/Zn) = E0(Zn2+/Zn) – RT/2F ln(1/[Zn2+(aq)]
The cell potential, Ecell = E(Cu2+/Cu) - E(Zn2+/Zn)
= E0(Cu2+/Cu) – RT/2F ln(1/[Cu2+(aq)] - E0(Zn2+/Zn) + RT/2F ln(1/[Zn2+(aq)]
= E0(Cu2+/Cu) -E0(Zn2+/Zn)- RT/2F ln(1/[Cu2+(aq)] + RT/2F ln(1/[Zn2+(aq)]
= E0(Cu2+/Cu) -E0(Zn2+/Zn)- RT/2F (ln(1/[Cu2+(aq)]- ln(1/[Zn2+(aq)])
Therefore, Nernst equation for Daniel cell is
Ecell = E0cell - RT/2F ln [Zn2+]/[Cu2+]
Ecell = E0cell − 2.303RT/2F ln [Zn2+]/[Cu2+]
by putting the value of R= 8.314J/KM ,T=298K, ln=2.303log and F=96457C
Ecell =E0cell − 0.059/2 log[Zn2+]/[Cu2+]
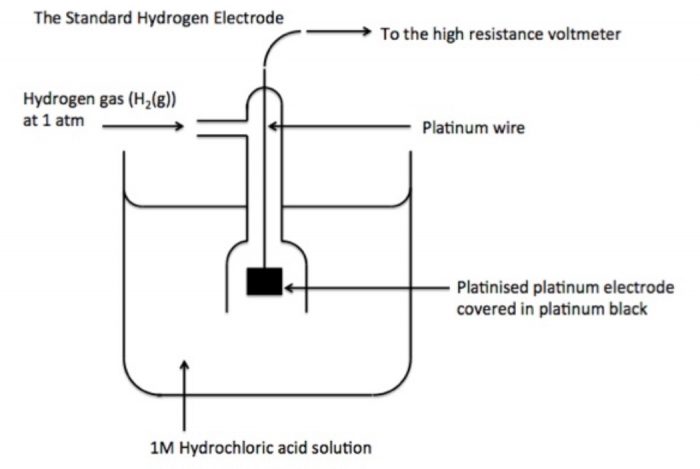
STANDARD HYDROGEN ELECTRODE (SHE)
ü It is reference electrode consists of a platinum electrode(Pt wire fitted in glass tube) in contact with H2 gas (1 atm) and aqueous H+ ions (1 M).
ü It is assigned 0.0 V electrode potential.
ü It may behave as anodic or cathodic half cell.
ü It is represented as
Pt(s)|H2(g)(aH2= 1)|H+(aq)(aH+ = 1).
ü When SHE is coupled with an other half cell then cell potential is the value of the electrode potential of half cell.
EMF and Electrode Potential
EMF: (electromotive force): It is the electrode potential difference across the terminals of the cell when no current is drawn through the cell.
Electrode potential. It is the potential difference develops between the electrode and the electrolyte.
Standard electrode potential : When the concentrations of all the species involved in a half-cell is unity then the electrode potential is known as standard electrode potential.Electrode potential
- More positive: Stronger oxidizing agent and more readily accepts electrons.
- More negative: Stronger reducing agent and more readily gives electrons.
- By combining two half cell reaction, we get a complete net reaction.
- The total cell potential (Ecell) is given by:
Ecell = Ecathode – Eanode
=Eright – E left
Saturday, January 1, 2022
Chemistry Practical Viva Part-1
1. What is the principle of volumetric analysis?
Answer. In volumetric analysis, the concentration of a solution is determined by allowing a known volume of the solution to react, quantitatively with another solution of known concentration.
2. What is titration ?
Answer. The process of adding one solution from the burette to another in the conical flask in order to complete the chemical reaction involved, is known as titration.
3. What is a standard solution ?
Answer. A solution whose strength is known is called a standard solution. 4. What is a normal solution ?
Answer. A solution containing one gram-equivalent mass of the solute per litre of the solution is called a normal solution.
5. What is indicator ?
Answer. Indicator is a chemical substance which changes colour at the end point
6. What is end point ?
Answer. The stage during titration at which the reaction is just complete is known as the end point of titration.
7. Why a titration flask should not be rinsed ? Answer. This is because during rinsing-some liquid will remain sticking to the titration flask therefore the pipetted volume taken in the titration flask will increase.
8. What are primary and secondary standard substances?
Answer. A substance is known as primary standard if it is available in high degree of purity, if it is stable and unaffected by air, if it does not gain or lose moisture in air, if it is readily soluble and its solution in water remains as such for long time. On the other hand, a substance which does not possess the above characteristics is called a secondary standard substance. Primary standards are crystalline oxalic add, anhydrous Na2CO3 , Mohr’s salt, etc.
9. Burette and pipette must be rinsed with the solution with which they are filled, why ?
Answer. The burette and pipette are rinsed with the solution with which they are filled in order to remove any water sticking to their sides, which otherwise would decrease the cone, of the solutions to be taken in them
10.It is customary to read lower meniscus in case of colourless and transparent solutions and upper meniscus in case of highly coloured solutions, why ?
Answer. Because it is easy to read the lower meniscus in case of colourless solutions, while the upper meniscus in case of coloured solutions. In case of coloured solutions lower meniscus is not visible clearly.
11.What is a molar solution ?
Answer. A molar solution is a solution, a litre of which contains one gm-mole of the substance. This is symbolised as 1M.
12.Why the last drop of solution must not be blown out of a pipette?
Answer. Since the drops left in the jet end is extra of the volume measured by the pipette.
13.Pipette should never be held from its bulb, why ?
Answer. The body temperature may expand the glass and introduce an error in the measurement volume.
14. What is permanganometry ?
Answer. Redox titrations involving KMnO4 as the oxidising agent are called permanganometric titrations.
15.Which is an oxidising agent and a reducing agent in the reaction between KMnO4 and FeSO4?
Answer. KMnO4 acts as oxidising agent and FeSO4 acts as reducing agent.
16.What is the indicator used in KMnO4 titration ?
Answer. No indicator is used because KMnO4 acts as a self-indicator
17.Why does KMnO4 act itself as an indicator ?
Answer. In the presence of dilute sulphuric acid, KMnO4 reacts with reducing agent (oxalic acid or . ferrous sulphate). When all the reducing agent has been oxidised, the excess of KMnO4 is not decomposed and imparts pink colour to the solution.
18.What is the end point in KMnO4 titrations ? Answer. From colourless to permanent light pink.
19.Why is Mohr’s salt preferred as a primary standard over ferrous sulphate in volumetric analysis ?
Answer. This is because of the fact that Mohr’s salt is stable and is not readily oxidised by air. Ferrous sulphate gets oxidised to ferric sulphate.
20. Why are a few drops of dilute sulphuric acid added while preparing a standard solution of Mohr’s salt ?
Answer. Few drops of H2SO4 are added to prevent the hydrolysis of ferrous sulphate.
21.Why a burette with rubber pinch cock should not be used in KMnO4 titrations ? Answer. Because KMnO4 attacks rubber.
22.Sometimes a brown ppt. is observed in KMnO4 titrations. Why ?
Answer. It is due to insufficient quantity of dil. sulphuric acid. Brown coloured ppt. (MnO2.H20) is formed due to the incomplete oxidation of KMnO4.
23.Why should you heat the oxalic acid solution to about 60-70°C before titrating with KMnO4 solution ?
Answer. In cold, the reaction is very slow due to the slow formation of Mn 2+ ions. Oxalic acid is heated to speed up the liberation of Mn 2+ ions which then autocatalyses the reaction and thus the reaction proceeds rapidly. This also serves the purpose of expelling the carbondioxide evolved during the reaction which otherwise does not allow the reaction to go to completion.
24.What is the equivalent mass of KMnO4 when it acts as oxidizing agent in acidic medium ?
Answer. KMnO4 loses 5 electrons per molecule, when it acts as oxidizing agent in the presence of acids. Therefore, its equivalent mass is one-fifth of its molecular mass.
25.Are ‘molality’ and “molarity’’ same ?
Answer. No, molality of a solution is defined as the number of moles of solute present in 1000 grams of the solution whereas molarity tells us about the number of moles of the solute present per litre of the solution.
26.What is the basicity of H2SO4 ?
Answer. 2.
feature post
Study materials for CPDT IGNOU BSE-061
Q. Students join Jawahar Navodaya school from various backgrounds such as caste, gender and religion. Some of them might also have disabil...