1. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions: 5 × 1 = 5 marks
The adjective “Crystalline” when applied to solids, implies an ideal crystal
in which the structural units, termed as unit cells, are repeated regularly and
indefinitely in three dimensions in space. The unit cell, containing at least
one molecule, has a definite orientation and shape defined by the translational
vectors a, b and c. The unit cell therefore has a definite volume, V that
contains the atoms and molecules necessary for generating the crystal. Every
crystal can be classified as a member of one of the seven possible crystal
systems or crystal classes that are defined by the relationship between the
individual dimensions a, b and c of the unit cell and between the individual
angles, α, β and γ of the unit cell. The structure of the given crystal may be
assigned to one of the 7 crystal systems, to one of the 14 Bravais lattices.
Based on these observations, seven crystal systems were identified: triclinic,
monoclinic, trigonal or rhombohedral, tetragonal, hexagonal, rhombic or
orthorhombic and cubic.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
(i)The crystal system of a compound with unit cell dimensions,
a = 0.387 nm, b = 0.387 nm and c = 0.504 nm
and α = β = 900 and γ = 1200 is
(a) Cubic
(b) hexagonal
(c) orthorhombic
(d) rhombohedral
Ans- b
(ii)In a triclinic crystal
(a) a = b = c, α = β = γ = 900
(b) a ≠ b = c, α = β = γ = 900
(c) a ≠ b ≠ c, α ≠ β ≠ γ ≠ 900
(d) a ≠ b ≠ c, α = γ = 900, β≠ 900
Ans- c
(iii) The unit cell with dimensional a = b ≠ c, α = β = γ = 900 is
(a) Cubic
(b) triclinic
(c) hexagonal
(d) tetragonal
Ans- d
(iv). An example of orthorhombic crystal system is
(a) SnO2
(b) KNO3
(c) ZnO
(d) K2Cr2O7
Ans- b
(v) The number of atoms per unit cell of bcc structure is
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) 6
Ans-b
2. Read the passage given below and answer the following
questions:5 × 1 = 5 marks.
A Schottky
defect is an excitation of the site occupations in a crystal lattice leading to
point defects named after Walter H. Schottky. In elemental crystals it refers
to simple lattice vacancies, also called valency defects. In ionic crystals,
this defect forms when oppositely charged ions leave their lattice sites and
become incorporated for instance at the surface, creating oppositely charged
vacancies. These vacancies are formed in stoichiometric units, to maintain an
overall neutral charge in the ionic solid.
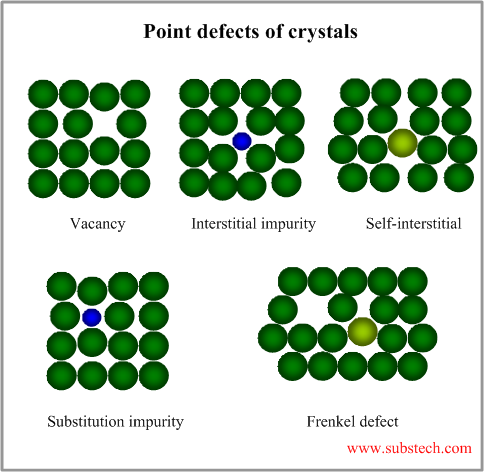
A Frenkel defect is a type of point defect in crystalline solids, named after its discoverer Yakov Frenkel. The defect forms when an atom or smaller ion (usually cation) leaves its place in the lattice, creating a vacancy and becomes an interstitial by lodging in a nearby location.[2] In elemental systems, they are primarily generated during particle irradiation, as their formation enthalpy is typically much higher than for other point defects, such as vacancies, and thus their equilibrium concentration according to the Boltzmann distribution is below the detection limit. In ionic crystals, which usually possess low coordination number or a considerable disparity in the sizes of the ions, this defect can be generated also spontaneously, where the smaller ion (usually the cation) is dislocated
(i) Schottky defect in crystals is observed when
(a)
an ion leaves its normal site and occupies an interstitial site
(b) unequal number of cations and
anions are missing from the lattice
(c) density of the crystal increases
(d) equal number of cations and anions are missing from the lattice
Ans- d
(ii)
Schottky defect generally appears in :
(a)
NaCl
(b) KCl
(c) CsCl
(d) all of these
Ans-d
(iii). Which of the following crystals does not
exhibit Frenkel defect?
(a) AgBr
(b) AgCl
(c) KBr
(d) ZnS
Ans- c
(iv). When electrons
are trapped into the crystal in anion vacancy, the defect is known as :
(a) Schottky defect
(b) Frenkel defect
(c) Stoichiometric defect
(d) F-centre
Ans-d
(v) The appearance of
colour in solid alkali metal halides is generally due to
(a) Schottky defect
(b)
Frenkel defect
(c) Interstitial positions
(d) F-centre
Ans-d
3.Read the passage and answer the questions given.
Solid is that form of matter which possess rigidity and hence a definite shape and a definite volume. If intermolecular forces are greater than thermal energy, substance exists as solid. Solids can be classified into two types. Crystalline solids and amorphous solids. Crystalline solids have regular arrangement of particles, definite geometrical shapes, sharp melting points and definite heat of fusion. On the other hand, amorphous solids have no regular arrangement of particles, irregular shapes, melt over a range of temperature and no definite heat of fusion. They are isotropic and under go irregular cleavage on cutting. Ionic solids, Molecular solids, Network covalent solids and metallic solids are other types of metallic solids.
i). A Solid is very hard, electrical insulator in solid as well as molten states and melts at high temperature. What type of solid is it?
a. Ionic
If you are looking for more information about flat rate locksmith Las Vegas check that right away. Samsung S21 Ultra case with S pen holder
ReplyDelete